Management of Risk or M_o_R 4 (aka MoR 4) is the latest edition of Management of Risk – a must-have certification for roles where managing risk is inherent, including portfolio, programme, project, business change and risk management professionals. Management of Risk 4 has a specific relevance for individuals working in product focussed environments / roles, offering a compelling integrated solution for the unique challenges faced by modern, digital-first organizations.
MoR 4 has been developed for candidates and practitioners who are interested in understanding how risk links to opportunity and the delivery of benefits, and in communicating or cascading this to stakeholders.



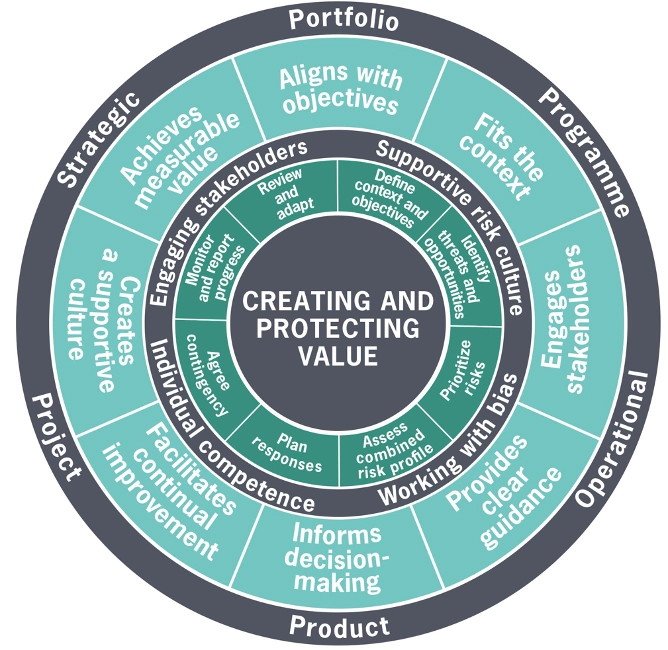
The first seven principles are enablers. The final principle is the result of implementing risk management well.
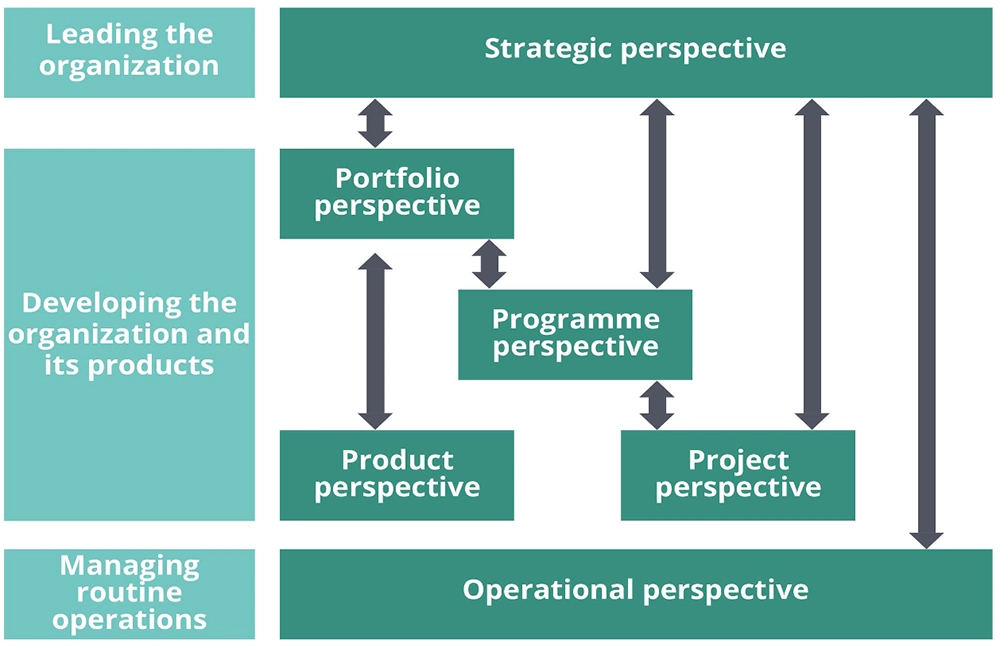
In order to allow the effective escalation, delegation and/or aggregation of risks and to identify and manage common themes within any organization it is very important to ensure that there is an integrated risk management approach across M_o_R perspectives.
Most organizations will not operate across all six perspectives, but all will have strategic and operational objectives, and most will have some objectives related to changing the organization or to the product development and management.
Individuals (in groups) interpret data in situations and make judgements (educated guesses) under uncertainty.
Given that people make the judgements and take the actions, risk management can never be successful if people considerations are ignored.
People considerations in risk management are addressed by M_o_R principles of engaging stakeholders and creating a supportive culture.

A structured set of activities that define the sequence of actions and their inputs and outputs to achieve a specific objective.


Management of Risk (M_o_R) certification trainings are provided by PeopleCert's Accredited Training Organizations (ATOs) across the globe. Tecknologia is also a PeopleCert Accredited Training Organization (ATO) offering Management of Risk (M_o_R) certification trainings across the globe and in various formats.
| Certification Level | Course Duration (Virtual Classroom) | Course Duration (Classroom) | Certificate Valid for |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoR Practitioner | 3 Days | 3 Days | 3 Years |
M_o_R 4 does not have a foundation level training and certification.
Click on the links for certification levels to explore the pre-requisites, exams and other details.

MoR stands for Management of Risk, M_o_R has been primarily designed to help organizations establish an effective framework for risk management which will enable them to make informed decisions about the risks that affect their strategic, portfolio, programme, project, product, and operational objectives.
Prices vary depending on the mode of delivery, location, deliverables and the quality of training delivery. Typically Management of Risk online training costs between £1400 and £2500.
MoR 4 Practitioner pass marks remain 33/60 (50%). Kindly note that there is no foundation level for M_o_R 4.
Management of Risk qualifications have helped tens of thousands of professionals globally enhance their skills and achieve their professional ambitions. Professionals holding MoR accreditation stand a better chance of being invited for an interview and definitely stand a better chance being offered a role afterwards.
M_o_R can be a very valuable addition to the list of professional qualifications and accreditations which can help achieve professional growth within organisations, without a need to switch jobs/ employers.
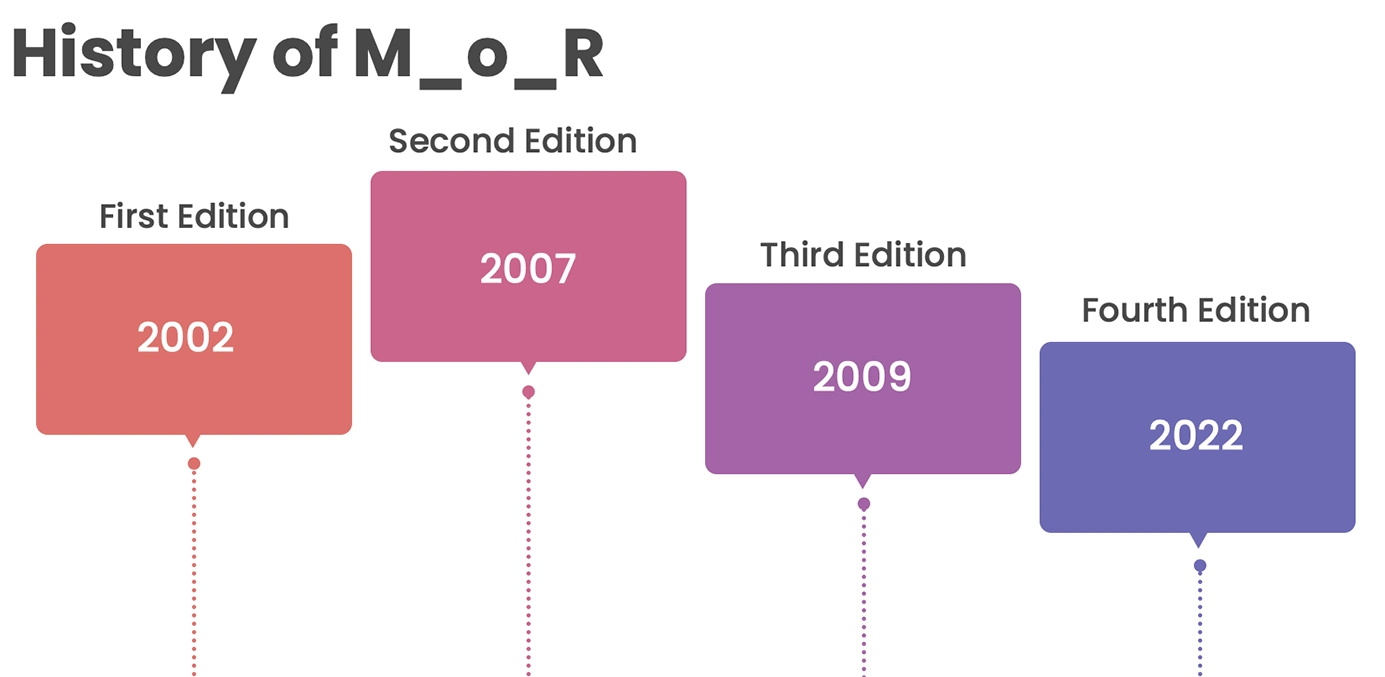
Management of Risk (M_o_R) has been, in the past, and is very much relevant today. MoR has been evolving ever since its inception and in late 2002, PeopleCert released Management of Risk 4th edition (aka M_o_R 4) in 2022 which addresses the needs and demands of risk management profession today and for coming years.
Management of Risk (M_o_R) is definitely a good choice for beginners who aim at pursuing a career in risk management and related disciplines. Having MoR qualifications early in the career can play the role of a catalyst when it comes to climbing the professional ladder.
While MoR practitioner exam is hard, it is not rocket science and anyone with correct level of attention, training and devotion can definitely achieve success in the exam.
MoR practitioner pass rate (across the market) remains around 80% globally, in first attempt. Tecknologia takes pride in maintaining 100% pass rate so far (May 2024).
It is absolutely possible to achieve M_o_R exam success while relying on self study. However, high standard MoR training can accelerate the process, along with exam success probability, for sure.
Management of Risk (M_o_R) Practitioner certification is considered to be professional qualifications only. These qualifications are widely recognised and sought after globally, however, they are not the same as a college or university degree. Some quarters believe that MoR Practitioner qualification is equivalent to UK NQF 5/6 - Tecknologia has no grounds to confirm this.
There is no negative marking in MoR exams. No marks are deducted for a wrong answer.
Management of Risk (MoR) Practitioner certifications has validity of 3 years from issuance date. Candidate must retake the exam within 3 years to maintain their certifications. Alternatively, candidates can log Continuous Professional Development points (CPDs) over three years, via paid PeopleCert membership, to maintain certifications.